It’s well understood that spiders have poor eyesight and thus sense the vibrations in their webs whenever prey (like a fly) gets caught; the web serves as an extension of their sensory system. But spiders also exhibit less-understood behaviors to locate struggling prey. Most notably, they take on a crouching position, sometimes moving up and down to shake the web or plucking at the web by pulling in with one leg. The crouching seems to be triggered when prey is stationary and stops when the prey starts moving.
But it can be difficult to study the underlying mechanisms of this behavior because there are so many variables at play when observing live spiders. To simplify matters, researchers at Johns Hopkins University’s Terradynamics Laboratory are building crouching spider robots and testing them on synthetic webs. The results provide evidence for the hypothesis that spiders crouch to sense differences in web frequencies to locate prey that isn’t moving—something analogous to echolocation. The researchers presented their initial findings today at the American Physical Society’s Global Physics Summit in Anaheim, California.
“Our lab investigates biological problems using robot physical models,” team member Eugene Lin told Ars. “Animal experiments are really hard to reproduce because it’s hard to get the animal to do what you want to do.” Experiments with robot physical models, by contrast, “are completely repeatable. And while you’re building them, you get a better idea of the actual [biological] system and how certain behaviors happen.” The lab has also built robots inspired by cockroaches and fish.
The research was done in collaboration with two other labs at JHU. Andrew Gordus’ lab studies spider behavior, particularly how they make their webs, and provided biological expertise as well as videos of the particular spider species (U. diversus) of interest. Jochen Mueller’s lab provided expertise in silicone molding, allowing the team to use their lab to 3D-print their spider robot’s flexible joints.
Crouching spider, good vibrations
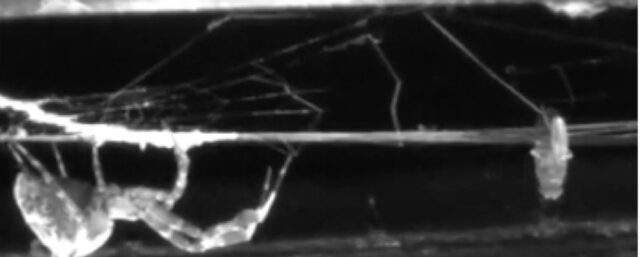
A spider exhibiting crouching behavior.
Credit:
YouTube/Terradynamics Lab/JHU
The first spider robot model didn’t really move or change its posture; it was designed to sense vibrations in the synthetic web. But Lin et al. later modified it with actuators so it could move up and down. Also, there were only four legs, with two joints in each and two accelerometers on each leg; real spiders have eight legs and many more joints. But the model was sufficient for experimental proof of principle. There was also a stationary prey robot.

